Electrodialysis (ED)
For value-added demineralization of process streams
For value-added demineralization of process streams
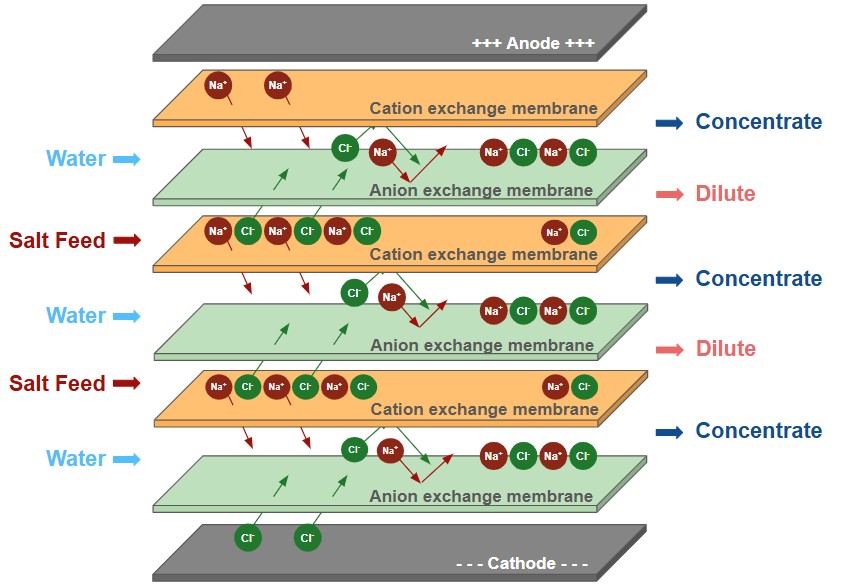
Using our proprietary ion exchange membranes, ED increases the quality and purity of your process stream by removing salts and other ionized components, keeping the valuable product.