E.C.O.Film Non-Phosphorus Cooling Water Technology
Reduce operational risk, achieve compliance with stricter environmental regulations, and address social challenges
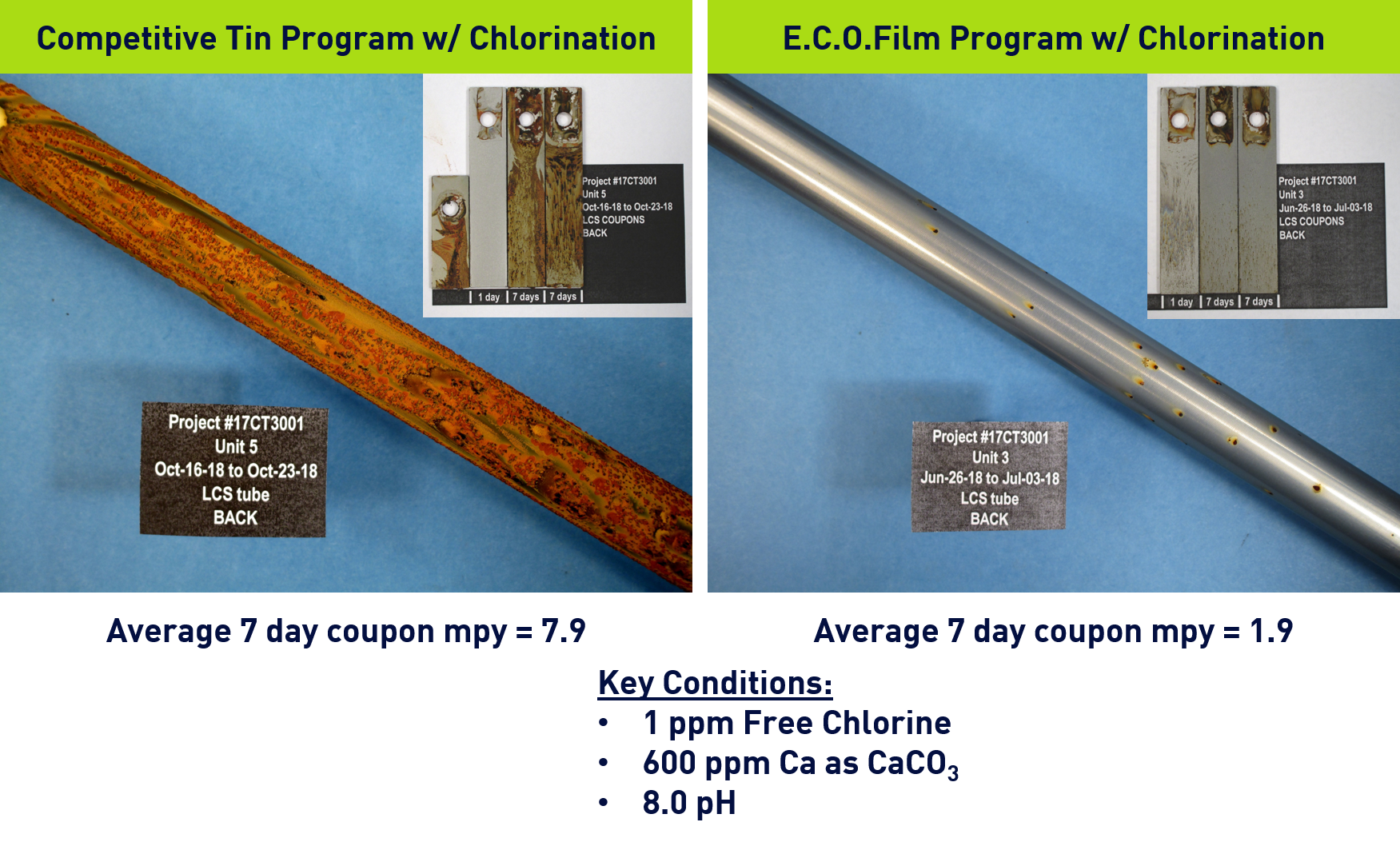
Deposition in critical cooling operations can limit production, algae growth can cause discharge violations and high biocide usage, and many customers now face increased phosphorus limits. Veolia's non-phosphorus1 cooling water treatment chemistry is designed to provide non-phosphorus mild steel corrosion protection and scale control in cooling systems.
Veolia's E.C.O.Film Technology
With a long history in technology development, Veolia is a leading innovator of non-phosphorus chemistry for cooling water. Through years of testing non-phosphorus corrosion inhibitors and developing refined treatment programs, Veolia has developed E.C.O.Film, or Engineered Carboxylate Oxide (E.C.O.), a technology that is designed to provide complete deposition (scale) and corrosion protection in open recirculating cooling water systems without the use of any phosphorus or EPA priority pollutant materials.
Removing the phosphate typically used for corrosion inhibition and deposit control eliminates the risk of costly calcium phosphate deposition, reduces the nutrient load in the water that can fuel biological and algae growth, and allows you to meet stricter phosphate discharge limits without the need for a costly equipment solution. The simplicity of the program improves safety, reduces acid usage and handling, reduces program and chemical feed complexity, and reduces chemical handling. E.C.O.Film is the only cooling water product available that helps customers address social challenges, and brand and community image with a new approach to chemistry and minimal impact on the environment around the customer.
E.C.O.Film Chemistry
The E.C.O.Film Package
Impact on your Operation
Performance
LSP Whitewater reduces phosphorus discharge with E.C.O.Film non-phosphorus cooling water treatment
LSP Whitewater, a cogeneration power plant located in Wisconsin, needed to significantly reduce the phosphorus output of their cooling water treatment program to meet local regulatory restrictions. To avoid a $1.8M capital expenditure, LSP Whitewater turned to Veolia’s E.C.O.Film non-phosphorus cooling water treatment to provide an alternative solution that would eliminate phosphorus from their cooling water program, while maintaining mild steel corrosion rate and overall system performance.
1May contain trace amounts.